Academic Administration Model to Promote Active Learning Management of Small Schools under Suratthani Primary Education Service Area Office 3
Main Article Content
Abstract
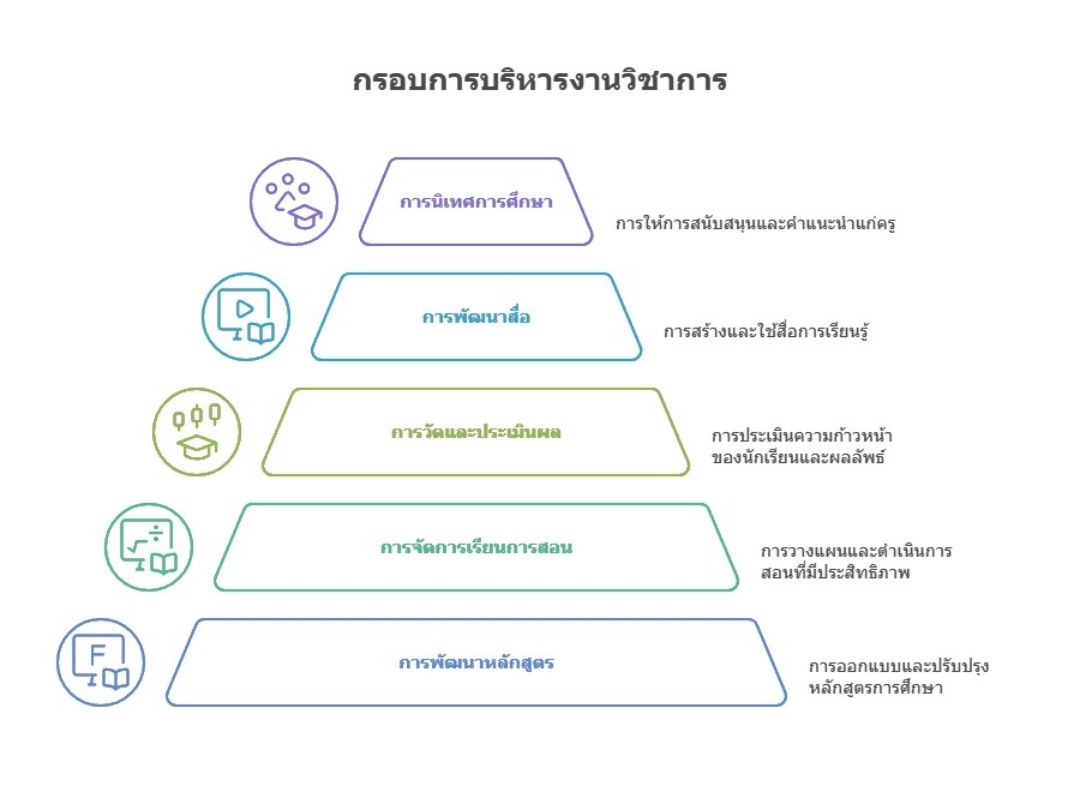
This research article aims to (1) study the components of academic management to promote proactive learning in small schools, (2) develop a model of academic management to enhance proactive learning in small schools, and (3) evaluate the model of academic management to support proactive learning in small schools under the Surat Thani Primary Education Service Area Office 3. This study employs a mixed-methods research design with three steps: (1) studying the components of academic management to promote proactive learning in small schools, with a sample of 100 school administrators and academic heads selected using the Krejcie and Morgan table; (2) developing a model of academic management to enhance proactive learning in small schools through discussions with 8 selected experts; and (3) evaluating the model of academic management to support proactive learning in small schools, again with a sample of 100 school administrators and academic heads determined using the Krejcie and Morgan table. The tools used for data collection include a questionnaire on the components of academic management, a suitability and consistency checklist, and an evaluation form. The statistical methods used in the research include mean, standard deviation, and content analysis. The research findings reveal that: 1) the components of academic management to promote proactive learning in small schools consist of five aspects: curriculum development and implementation, teaching and learning management, assessment and evaluation, development of educational media and technology, and educational supervision; 2) the development results of the academic management model to promote proactive learning in small schools indicate that the model comprises five components: principles, objectives, implementation methods, evaluation guidelines, and success conditions; and 3) the evaluation results of the model show that feasibility, usefulness, and accuracy are at a high level, while suitability is at the highest level.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
จันทร์จิรา จันทร์โกมุท. (2566). ผู้อำนวยการโรงเรียนบ้านไทรห้อง. สัมภาษณ์. 11 กรกฎาคม.
ชัยสิทธิ์ จุลนิล. (2566). รองผู้อำนวยการสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาสุราษฎร์ธานี เขต 3. สัมภาษณ์. 11 กรกฎาคม.
ทิศนา แขมมณี. (2555). ศาสตร์การสอน : องค์ความรู้เพื่อการจัดกระบวนการเรียนรู้ที่มีประสิทธิภาพ. (พิมพ์ครั้งที่16).กรุงเทพมหานคร : จุฬาลงกรณ์มหาวิทยาลัย.
บุญชม ศรีสะอาด. (2560). การวิจัยเบื้องต้น ฉบับปรับปรุงใหม่. (พิมพ์ครั้งที่10). กรุงเทพฯ: สุวีริยาสาส์น.
ปรีดา บัวยก. (2564). รูปแบบการบริหารงานวิชาการเพื่อยกระดับผลสัมฤทธิ์ทางการเรียนของโรงเรียน สังกัดเทศบาลนคร สุราษฎร์ธานี จังหวัดสุราษฎร์ธานี. (ครุศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต, มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสุราษฎร์ธานี).
สมัย ชารมาลย์. (2559). รูปแบบการบริหารงานวิชาการที่มีประสิทธิผลของโรงเรียนเอกชน ประเภทสามัญศึกษาในภาคตะวันออกเฉียงเหนือ. (ครุศาสตรดุษฎีบัณฑิต, มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสกลนคร).
สุพัตรา แก้วมณี. (2563). การบริหารงานวิชาการเพื่อส่งเสริมการจัดการเรียนรู้เชิงรุกของผู้บริหารสถานศึกษาในโรงเรียนขนาดเล็ก สังกัดสำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษานครราชสีมา เขต 5. (ศึกษาศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต, มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏนครราชสีมา).
อรวรรณ สวัสดิ์. (2566). ศึกษานิเทศก์ สำนักงานเขตพื้นที่การศึกษาประถมศึกษาสุราษฎร์ธานี เขต 3. สัมภาษณ์. 11 กรกฎาคม.
อัศนีย์ สุกิจใจ. (2560). ภาวะผู้นำทางวิชาการของผู้บริหารสถานศึกษา. วารสารวิจัยพุทธศาสตร์, 3(1), 23-37.
Cronbach, Lee J. (1990). Essentials of Psychological Testing. (5th ed.). New York: Harper & Row.
Krejcie, R. V., & Morgan, D. W. (1970). Determining sample size for research activities. Educational and Psychological Measurement, 30(3), 607–610.