Good Governance Organization for Sustainable Development
Keywords:
Organization, Good Governance, Development, SustainableAbstract
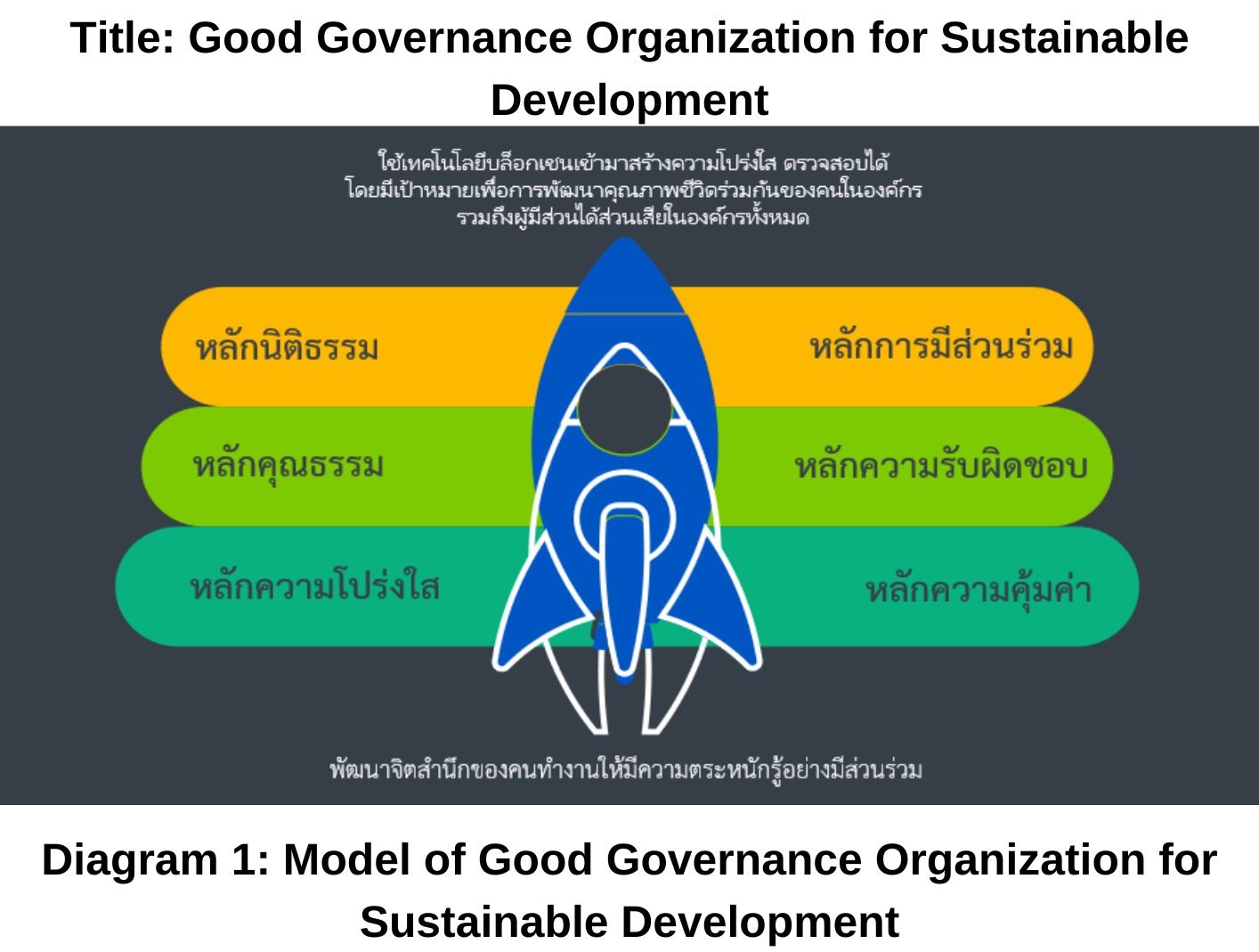
This research paper is a qualitative study through document analysis. Its objective is to study the Governance Organization for Sustainable Development. The study found that good governance requires appropriate and essential principles, including: 1) the rule of law, 2) integrity, 3) transparency, 4) participation, 5) accountability, and 6) cost-effectiveness. The implementation of these six principles to build a governance organization for sustainable development must be developed concurrently in all principles, starting with fostering the awareness of the employees to be participative, understanding, and recognizing their roles and responsibilities towards self-care and mutual care with empathy. It involves open-mindedness in listening to each other, communicating with kindness, being simple and straightforward, and being responsible for self-management, people management, and work management. There is accountability towards laws and organizational rules, readiness to disclose necessary information to stakeholders to create participation at all levels, considering cost-effectiveness in management in terms of time, resources, and quality of life. Technology or innovation is utilized to enhance transparency together, by incorporating these systems to store necessary information and continuously updating it to keep up with current changes. This benefits consensual decision-making within the organization, leading to a governance organization for sustainable development. The new knowledge derived from this research includes a model for a governance organization for sustainable development, which integrates governance principles as the core of development by promoting awareness to create shared consciousness in all principles. The goal is to develop the quality of life through participation by utilizing technology or innovation to create transparent and accountable systems.
References
ชัยสิทธิ์ สินสมบูรณ์ทอง. (2548). ผู้ว่าราชการจังหวัด CEO กับการพัฒนาบ้านเมืองให้น่าอยู่ควบคู่คุณธรรม. วารสารพัฒนบริหารศาสตร์, 45(2), 201-208.
ดวงตา ราชอาษา. (2558). แนวทางการขับเคลื่อนการบริหารตามหลักธรรมาภิบาลในยุคทุนนิยม. วารสารแพรวากาฬสินธุ์, 2(3), 130-149.
ทิวากร แก้วมณี. (2559). ธรรมาภิบาล = Good Governance. กรุงเทพฯ : บริษัทสำนักพิมพ์สยามปริทัศน์ จำกัด.
เทพศักดิ์ บุณยรัตพันธุ์. (2559). เอกสารการสอนชุดวิชาขอบข่ายการศึกษาและวิจัยทางรัฐประศาสนศาสตร์. นนทบุรี : มหาวิทยาลัยสุโขทัยธรรมาธิราช.
บวรศักดิ์ อุวรรณโณ. (2544). การสร้างธรรมาภิบาล. กรุงเทพฯ : สถาบันพระปกเกลา.
พระครูปลัดธวัชชัย ธวชฺชยเมธี (มั่งมีเพชร). (2566). ธรรมาภิบาล : พัฒนาสังคมไทยอย่างไรให้ยั่งยืน. วารสารสหวิทยาการนวัตกรรมปริทรรศน์, 6(2), 25-43.
พีรพล ไทยทอง. (2560). ธรรมาภิบาลกับการบริหารงานภาครัฐยุคใหม่ไทยแลนด์ 4.0. วารสาร มจร สังคมศาสตร์ปริทรรศน์, 6(2), 607-615.
รินทร์ลภัส วุฒิปรีชาสิทธิ์. (2562). แนวทางการพัฒนาธรรมาภิบาลในการปฏิบัติงานของหน่วยงานภาครัฐ. รัฐประศาสนศาสตรมหาบัณฑิต. คณะรัฐประศาสนศาสตร์ : สถาบันบัณฑิตพัฒนบริหารศาสตร์.
Chapman, R.A. (2000). Ethics in the Public Service for the New Millennium. Aldershot: Ashgate Publishing Company.
Cheung, A.B.L. and Scott, I. (2001). Governance and Public Sector Reform in Asia. New York, Routledge.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Institute of Sufficiency Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



