Motivation according to Moderate Postmodern Philosophy
Keywords:
Motivation, Postmodern, Moderate Postmodern PhilosophyAbstract
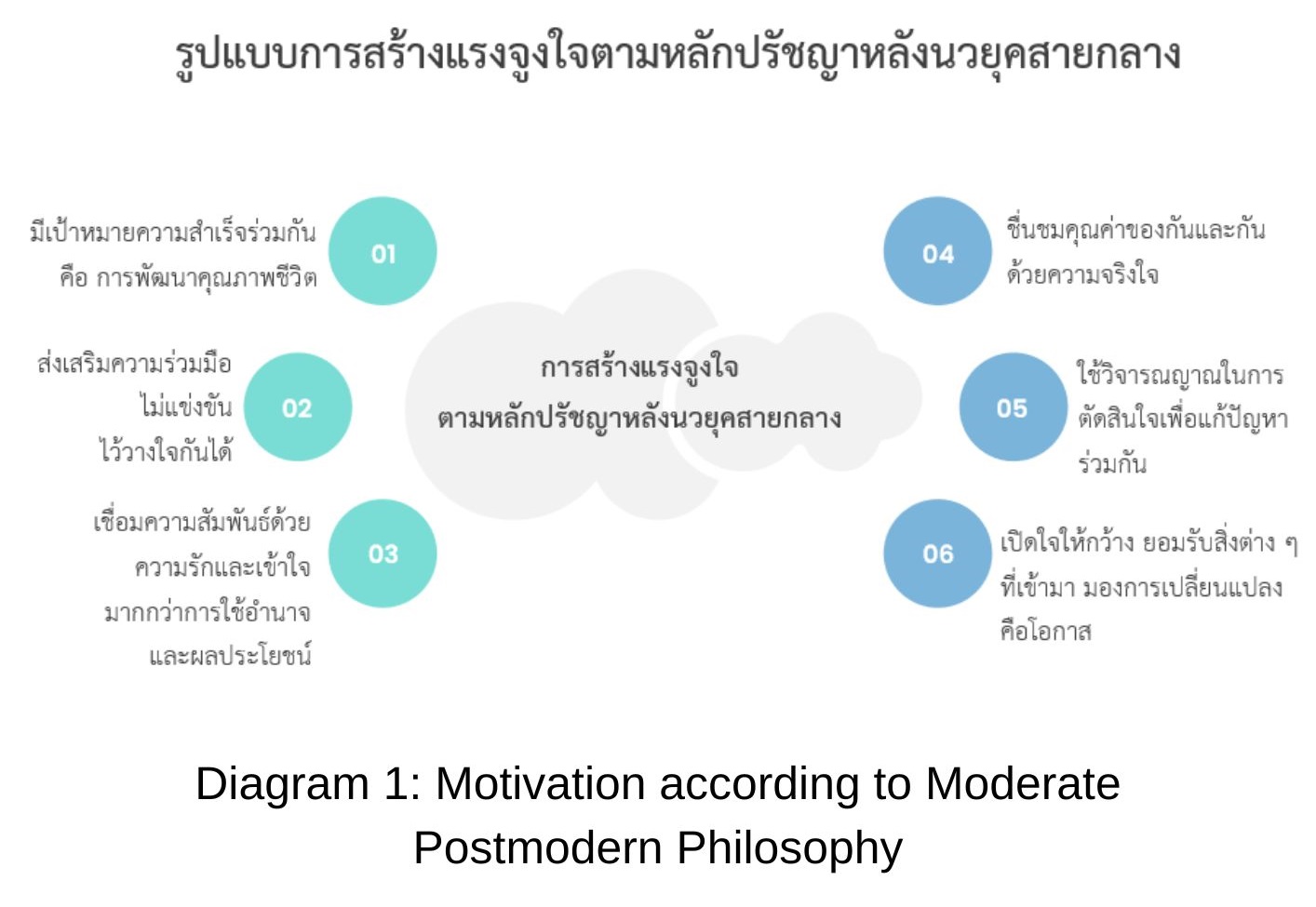
This research article utilizes qualitative research methodology through document analysis. Its aim is to analyze motivational forces based on postmodern philosophical principles. The research findings indicate that motivation is a psychological impetus that drives individuals towards their intended goals. Motivation according to postmodern philosophical principles involves motivational strategies that rely on rationality, including analysis, value assessment for decision-making, and their application. This is used to differentiate and evaluate various aspects using intelligence from different paradigms. The objective is to understand the goal of happiness, which serves as a guiding principle for the extent and quality of happiness, forming the foundational basis for motivational thinking. Therefore, the motivation that arises promotes the cultivation of intellectual potential, ethics, and morality, fostering emotional and cognitive development. Goals must be set for the collective well-being and the enhancement of the quality of life for oneself and others through the powers of creativity, adaptivity, collaborativity, and requisitivity
References
กีริติ บุญเจือ และคณะ. (2560). “ปรัชญาธรรมาภิบาลที่สนับสนุนพระปฐมบรมราชโองการ”. รายงานวิจัย. บัณฑิตวิทยาลัย : มหาวิทยาลัยราชภัฏสวนสุนันทา.
ชัยโรจน์ นพเฉลิมโรจน์. (2564). การคิดนวัตกรรมด้วยหลักการทรงงานตามหลักปรัชญาหลังนวยุค. วารสารการวิจัยเพื่อพัฒนาชุมชน, 15(2), 111-117.
เมธา หริมเทพาธิป. (2561). การมีส่วนร่วมในมุมมองหลังนวยุค. รมยสาร, 16(3), 63-77.
________. (2563). การจูงใจตนเองในแนวทางหลังนวยุค. วารสารพุทธมัคค์, 5(1), 99-107.
รัตติกรณ์ จงวิศาล. (2564). จิตวิทยาองค์กร. (พิมพ์ครั้งที่ 5). กรุงเทพฯ : บริษัท เอเชีย ดิจิตอลการพิมพ์ จำกัด.
อรพิน และคณะ. (2542). การพัฒนาแบบวัดแรงจูงใจภายใน. กรุงเทพฯ : สถาบันวิจัยพฤติกรรมศาสตร์ มหาวิทยาลัยศรีนครินทรวิโรฒ.
Carter, W. R., Nesbit, Paul L., Badham, R.J., Parker, K.S., and Sung, K.L. (2018). The effects of employee engagement and self-efficacy on job performance: a longitudinal field study, The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 29(17), 2483-2502.
Lai, MC., and Chen, Y.C.. (2012). Self-Efficacy, Effort, Job Performance, Job Satisfaction, and Turnover intention: The Effect of Personal Characteristics on Organization Performance. International Journal of Innovation, Management and Technolog., 3(4), 387-391.
Robbins, S. P., and Judge, T.A. (2017). Organizational Behavior. (17th ed). Boston : Pearson.
Themanson, J.R., and Rosen, J.P. (2015). Examining the relationships between self- efficacy, task-relevant attentional control, and task performance: Evidence from event-related brain potentials. British Journal of Psychology, 106(2), 253-271.
Tierney, P., & Farmer, S. M. (2011). Creative self-efficacy development and creative performance over time. Journal of Applied Psychology, 96(2), 277-293.
Woodhouse, G. Tacey, F. and Karen, J.W. (2013). To investigate the concerns and benefits of job sharing a community based Clinical Nurse Consultant role. Australian Journal of Advanced Nursing, 30(3), 33-40.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Institute of Sufficiency Journal

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.



